Bluetooth module has four output pins, namely, Lout, Rout, Vcc and GND. Right channel (Rout) and left channel (Lout) are connected to pins 2 and 7 of IC2, respectively, followed by presets VR1 and VR2, and capacitors C3 and C5. Pins 3 and 6 of IC2 are connected to feedback capacitors C4 and C6, which are grounded. Bluetooth module is given a power supply of 5V DC .
Connect amplifier to speakers
Output pins 11 and 12 of amplifier IC2 are directly connected to a loudspeaker (LS2). Similar configuration is done with output pins 15 and 16 of IC2 and another loudspeaker (LS1). A capacitor in series with a resistor is connected to each wire for preventing audio signal oscillation.
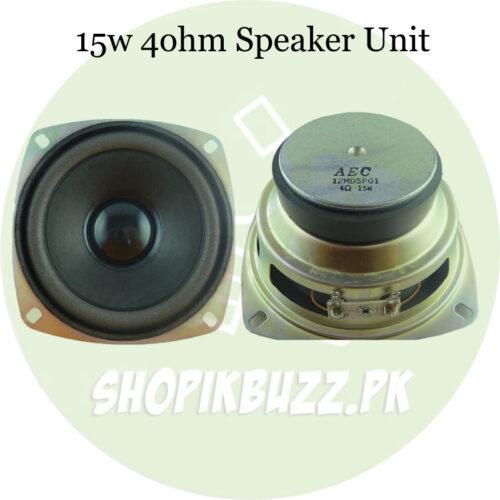
The parts of a speaker are:
- The cone and the dust cap (the parts that move air and produce sound)
- The spider and the surround (also called the suspension, these are the parts that hold the cone in place while still allowing them to move)
- The magnet and the voice coil (the parts that interact to convert electric energy into motion)
- The basket
- The pole and top plate
- And finally the frame that mounts everything together
How do speakers work?
Speakers work by converting
electrical energy into
mechanical energy (motion). The mechanical energy compresses air and converts the motion into sound energy or sound pressure level (SPL).
When an electric current is sent through a coil of wire, it induces a magnetic field.
In speakers, a current is sent through the voice coil which produces an electric field that interacts with the magnetic field of the permanent magnet attached to the speaker.
Like charges repel each other and different charges attract. As an audio signal is sent through the voice coil and the musical waveform moves up and down, the voice coil is attracted and repelled by the permanent magnet.
This makes the cone that the voice coil is attached to move back and forth. The back and forth motion creates pressure waves in the air that
we perceive as sound.